Portsmouth, New Hampshire on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Portsmouth is a city in

 At the town's incorporation in 1653, it was named "Portsmouth" in honor of the colony's founder, John Mason. He had been captain of the English port of
At the town's incorporation in 1653, it was named "Portsmouth" in honor of the colony's founder, John Mason. He had been captain of the English port of
 According to the
According to the

 * USS ''Albacore'' Museum & Park – a museum featuring the USS ''Albacore'', a U.S. Navy submarine used for testing, which was decommissioned in 1972 and moved to the park in 1985. The submarine is open for tours.
* Buckminster House – built in 1725, formerly a funeral parlor.
* Discover Portsmouth Center – visitor center, gallery, gift shop, John Paul Jones Historic House, walking tours, short film on the history of Portsmouth; operated by the Portsmouth Historical Society.
* The Music Hall – a 900-seat theater originally opened in 1878. The theater is now run by a non-profit organization and is fully restored. The venue hosts musical acts, theater, dance and cinema.
* New Hampshire Theatre Project – founded in 1986, a non-profit theater organization producing contemporary and classical works, and offering educational programs.
* North Church – historic church, the steeple of which is visible from most of Portsmouth
* Pontine Theatre – produces original theater works based on the history, culture and literature of New England at their 50-seat black box venue.
*The Player's Ring Theater – a black-box theater that produces original work from local playwrights.
*
* USS ''Albacore'' Museum & Park – a museum featuring the USS ''Albacore'', a U.S. Navy submarine used for testing, which was decommissioned in 1972 and moved to the park in 1985. The submarine is open for tours.
* Buckminster House – built in 1725, formerly a funeral parlor.
* Discover Portsmouth Center – visitor center, gallery, gift shop, John Paul Jones Historic House, walking tours, short film on the history of Portsmouth; operated by the Portsmouth Historical Society.
* The Music Hall – a 900-seat theater originally opened in 1878. The theater is now run by a non-profit organization and is fully restored. The venue hosts musical acts, theater, dance and cinema.
* New Hampshire Theatre Project – founded in 1986, a non-profit theater organization producing contemporary and classical works, and offering educational programs.
* North Church – historic church, the steeple of which is visible from most of Portsmouth
* Pontine Theatre – produces original theater works based on the history, culture and literature of New England at their 50-seat black box venue.
*The Player's Ring Theater – a black-box theater that produces original work from local playwrights.
*
Whaling Wall endangered
" September 14, 2010, Seacoast Online *Four public sculptures carved by Cabot Lyford stand in the city, including "The Whale" and "My Mother the Wind," a seven-ton blank granite statue which was installed on Portsmouth's waterfront in 1975. * Portsmouth African Burying Ground – a memorial park and the only archeologically verified 18th-century African burying ground in New England.
 * Richard Jackson House (1664)
*
* Richard Jackson House (1664)
*
Print
* '' The New Hampshire Gazette'' * ''
Greater Portsmouth Chamber of Commerce
{{authority control Cities in New Hampshire Cities in Rockingham County, New Hampshire Former colonial and territorial capitals in the United States Populated places established in 1630 Populated coastal places in New Hampshire 1630 establishments in the Thirteen Colonies
Rockingham County, New Hampshire
Rockingham County is a county in the U.S. state of New Hampshire. At the 2020 census, the population was 314,176, making it New Hampshire's second-most populous county. The county seat is Brentwood. Rockingham County is part of the Boston-Ca ...
, United States. At the 2020 census it had a population of 21,956. A historic seaport
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
and popular summer tourist destination on the Piscataqua River
The Piscataqua River (Abenaki: ''Pskehtekwis'') is a tidal river forming the boundary of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine from its origin at the confluence of the Salmon Falls River and Cochecho River. The drainage basin of the river ...
bordering the state of Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
, Portsmouth was formerly the home of the Strategic Air Command's Pease Air Force Base
Pease, in Middle English, was a noun referring to the vegetable pea; see that article for its etymology. The word survives into modern English in pease pudding.
Pease may also refer to:
People
* Pease family (Darlington), a prominent family in D ...
, since converted to Portsmouth International Airport at Pease
Portsmouth International Airport at Pease , formerly known as Pease International Airport, is a joint civil and military use airport located one nautical mile (2 km) west of the central business district of Portsmouth, a city in Rockingham ...
.
History
American Indians of theAbenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pre ...
and other Algonquian languages
The Algonquian languages ( or ; also Algonkian) are a subfamily of indigenous American languages that include most languages in the Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically simi ...
-speaking nations, and their predecessors, inhabited the territory of coastal New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
for thousands of years before European contact.
The first known European to explore and write about the area was Martin Pring
Martin Pring (1580–1626) was an English explorer from Bristol, England who in 1603 at the age of 23 was captain of an expedition to North America to assess commercial potential; he explored areas of present-day Maine, New Hampshire, and Cape Co ...
in 1603. The Piscataqua River is a tidal estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
with a swift current, but forms a good natural harbor. The west bank of the harbor was settled by European colonists in 1630 and named Strawbery Banke, after the many wild strawberries growing there. The village was protected by Fort William and Mary
Fort William and Mary was a colonial fortification in Britain's worldwide system of defenses, defended by soldiers of the Province of New Hampshire who reported directly to the royal governor. The fort, originally known as "The Castle," was situ ...
on what is now New Castle Island. Strategically located for trade between upstream industries and mercantile interests abroad, the port prospered. Fishing, lumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
and shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befo ...
were principal businesses of the region. Enslaved Africans
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
were imported
An import is the receiving country in an export from the sending country. Importation and exportation are the defining financial transactions of international trade.
In international trade, the importation and exportation of goods are limited ...
as laborers as early as 1645 and were integral to building the city's prosperity. Portsmouth was part of the Triangle Trade
Triangular trade or triangle trade is trade between three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. It has been used to offset t ...
, which made significant profits from slavery.

 At the town's incorporation in 1653, it was named "Portsmouth" in honor of the colony's founder, John Mason. He had been captain of the English port of
At the town's incorporation in 1653, it was named "Portsmouth" in honor of the colony's founder, John Mason. He had been captain of the English port of Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
, Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
, after which New Hampshire is named.
When Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War (1702–1713) was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in North America involving the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and Spain; it took place during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In E ...
ended in 1712, Governor Joseph Dudley
Joseph Dudley (September 23, 1647 – April 2, 1720) was a colonial administrator, a native of Roxbury in Massachusetts Bay Colony, and the son of one of its founders. He had a leading role in the administration of the Dominion of New England ...
selected the town to host negotiations for the 1713 Treaty of Portsmouth
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pers ...
, which temporarily ended hostilities between the Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pre ...
Indians and the colonies of Massachusetts Bay
Massachusetts Bay is a bay on the Gulf of Maine that forms part of the central coastline of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
Description
The bay extends from Cape Ann on the north to Plymouth Harbor on the south, a distance of about . Its ...
and New Hampshire.
In 1774, in the lead-up to the Revolution
In political science, a revolution (Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due ...
, Paul Revere
Paul Revere (; December 21, 1734 O.S. (January 1, 1735 N.S.)May 10, 1818) was an American silversmith, engraver, early industrialist, Sons of Liberty member, and Patriot and Founding Father. He is best known for his midnight ride to a ...
rode to Portsmouth warning that the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
was coming to capture the port. Although Fort William and Mary
Fort William and Mary was a colonial fortification in Britain's worldwide system of defenses, defended by soldiers of the Province of New Hampshire who reported directly to the royal governor. The fort, originally known as "The Castle," was situ ...
protected the harbor, the Patriot government moved the capital inland to Exeter, which ensured that it would be under no threat from the Royal Navy, which bombarded Falmouth (now Portland, Maine
Portland is the largest city in the U.S. state of Maine and the seat of Cumberland County. Portland's population was 68,408 in April 2020. The Greater Portland metropolitan area is home to over half a million people, the 104th-largest metropo ...
) instead on October 18, 1775. Portsmouth was the destination for several of Beaumarchais's ships containing materiel
Materiel (; ) refers to supplies, equipment, and weapons in military supply-chain management, and typically supplies and equipment in a commercial supply chain context.
In a military context, the term ''materiel'' refers either to the specif ...
, such as artillery, tents, and gunpowder, to help the American revolutionary effort. African Americans helped defend Portsmouth and New England during the war. In 1779, 19 enslaved African Americans from Portsmouth wrote a petition to the state legislature and asked that it abolish slavery, in recognition of their war contributions and in keeping with the principles of the Revolution. Their petition was not answered, but New Hampshire later abolished slavery.
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was previously the natio ...
's 1807 embargo
Economic sanctions are commercial and financial penalties applied by one or more countries against a targeted self-governing state, group, or individual. Economic sanctions are not necessarily imposed because of economic circumstances—they m ...
against American trade with Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
severely disrupted New England's trade with Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, and several local businessmen went bankrupt. Portsmouth was host to numerous privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
. In 1849, Portsmouth was incorporated as a city.
Once one of the nation's busiest ports and shipbuilding cities, Portsmouth expressed its wealth in fine architecture. It has significant examples of Colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 au ...
, Georgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
, and Federal style houses, some of which are now museums. Portsmouth's heart has stately brick Federalist stores and townhouses, built all-of-a-piece after devastating early 19th-century fires. The worst was in 1813 when 244 buildings burned. A fire district was created that required all new buildings within its boundaries to be built of brick with slate roofs; this created the downtown's distinctive appearance. The city was also noted for the production of boldly wood-veneered Federalist furniture, particularly by the master cabinet maker
A cabinet is a case or cupboard with shelves and/or drawers for storing or displaying items. Some cabinets are stand alone while others are built in to a wall or are attached to it like a medicine cabinet. Cabinets are typically made of wood (so ...
Langley Boardman.
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
spurred economic growth in New Hampshire mill towns such as Dover, Keene, Laconia, Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
, Nashua Nashua may refer to:
* Nashaway people, Native American tribe living in 17th-century New England
Places
In Australia:
* Nashua, New South Wales
In the United States:
* Nashua, California
* Nashua, Iowa
* Nashua, Minnesota
* Nashua, Kansas City ...
and Rochester
Rochester may refer to:
Places Australia
* Rochester, Victoria
Canada
* Rochester, Alberta
United Kingdom
*Rochester, Kent
** City of Rochester-upon-Medway (1982–1998), district council area
** History of Rochester, Kent
** HM Prison ...
, where rivers provided water power for the mills. It shifted growth to the new mill towns. The port of Portsmouth declined, but the city survived Victorian-era doldrums, a time described in the works of Thomas Bailey Aldrich
Thomas Bailey Aldrich (; November 11, 1836 – March 19, 1907) was an American writer, poet, critic, and editor. He is notable for his long editorship of ''The Atlantic Monthly'', during which he published writers including Charles W. Chesnutt. ...
, particularly in his 1869 novel ''The Story of a Bad Boy
''The Story of a Bad Boy'' (1870) is a semi-autobiographical novel by American writer Thomas Bailey Aldrich, fictionalizing his experiences as a boy in Portsmouth, New Hampshire. The book is considered the first in the "bad boy" genre of litera ...
''.
In the 20th century, the city founded a Historic District Commission, which has worked to protect much of the city's irreplaceable architectural legacy. In 2008, the National Trust for Historic Preservation named Portsmouth one of the "Dozen Distinctive Destinations". The compact and walkable downtown on the waterfront draws tourists and artists, who each summer throng the cafes, restaurants and shops around Market Square. Portsmouth annually celebrates the revitalization of its downtown (in particular Market Square) with Market Square Day, a celebration dating back to 1977, produced by the non-profit Pro Portsmouth, Inc.
Portsmouth shipbuilding history has had a long symbiotic relationship with Kittery, Maine
Kittery is a town in York County, Maine, United States. Home to the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard on Seavey's Island, Kittery includes Badger's Island, the seaside district of Kittery Point, and part of the Isles of Shoals. The southernmost town i ...
, across the Piscataqua River. In 1781–1782, the naval hero John Paul Jones
John Paul Jones (born John Paul; July 6, 1747 July 18, 1792) was a Scottish-American naval captain who was the United States' first well-known naval commander in the American Revolutionary War. He made many friends among U.S political elites ( ...
lived in Portsmouth while he supervised construction of his ship ''Ranger'', which was built on nearby Badger's Island
Badger's Island is located in the Piscataqua River at Kittery, Maine, directly opposite Portsmouth, New Hampshire. It carries U.S. Route 1 between the states, connecting to the Kittery mainland by the Badger's Island Bridge, and to New Hampshire b ...
in Kittery. During that time, he boarded at the Captain Gregory Purcell house, which now bears Jones' name, as it is the only surviving property in the United States associated with him. Built by the master housewright Hopestill Cheswell, an African American, it has been designated as a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
. It now serves as the Portsmouth Historical Society Museum.
The Portsmouth Naval Shipyard
The Portsmouth Naval Shipyard, often called the Portsmouth Navy Yard, is a United States Navy shipyard in Kittery on the southern boundary of Maine near the city of Portsmouth, New Hampshire.
Founded in 1800, PNS is U.S. Navy's oldest continuo ...
, established in 1800 as the first federal navy yard, is on Seavey's Island
Seavey's Island, site of the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard, is located in the Piscataqua River in Kittery, Maine, opposite Portsmouth, New Hampshire. It encompasses .
History
What is today called Seavey's Island was originally five separate islands c ...
in Kittery, Maine. The base is famous for being the site of the 1905 signing of the Treaty of Portsmouth
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pers ...
which ended the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
. Though US President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
orchestrated the peace conference that brought Russian and Japanese diplomats to Portsmouth and the Shipyard, he never came to Portsmouth, relying on the Navy and people of New Hampshire as the hosts. Roosevelt won the 1906 Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiolog ...
for his diplomacy in bringing about an end to the War.
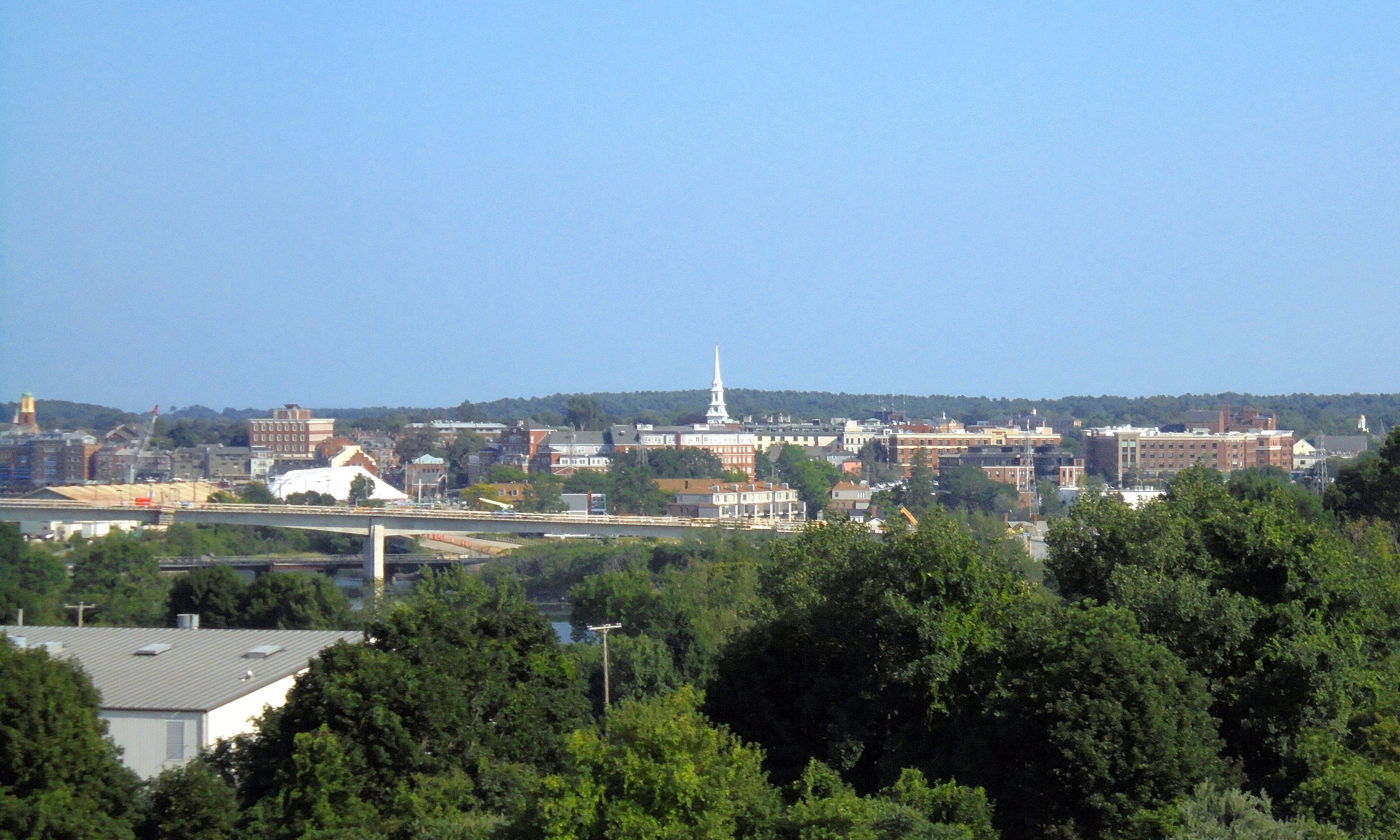
Geography
 According to the
According to the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
, the city has a total area of , of which are land and , or 6.92%, are water. Portsmouth is drained by Berrys Brook, Sagamore Creek and the Piscataqua River
The Piscataqua River (Abenaki: ''Pskehtekwis'') is a tidal river forming the boundary of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine from its origin at the confluence of the Salmon Falls River and Cochecho River. The drainage basin of the river ...
, which is the boundary between New Hampshire and Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
. The highest point in the city is above sea level, within Pease International Airport.
Climate
Portsmouth has ahumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(Dfb DFB may refer to:
* Deerfield Beach, Florida, a city
* Decafluorobutane, a fluorocarbon gas
* Dem Franchize Boyz, former hip hop group, Atlanta, Georgia
* Dfb, Köppen climate classification for Humid continental climate
* Distributed-feedback ...
) in spite of its maritime position, due to prevailing inland winds. Summers are moderately warm with winter days averaging around the freezing point, but with cold nights bringing it below the required isotherm to have a humid continental climate. With high year-round precipitation, the cold winters can often be very snowy and summers wet.
Demographics
Portsmouth is the sole city in Rockingham County, but the fourth-largest municipality, with fewer people than the towns of Derry, Londonderry, and Salem. As of the census of 2010, there were 21,233 people, 10,014 households, and 4,736 families residing in the city. The population density was 1,361.1 people per square mile (524.4/km). There were 10,625 housing units at an average density of 681.1 per square mile (262.3/km). Theracial makeup
A race is a categorization of humans based on shared physical or social qualities into groups generally viewed as distinct within a given society. The term came into common usage during the 1500s, when it was used to refer to groups of variou ...
of the city was 91.5% White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White o ...
, 1.7% African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 0.2% Native American, 3.5% Asian
Asian may refer to:
* Items from or related to the continent of Asia:
** Asian people, people in or descending from Asia
** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia
** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asi ...
, 0.01% Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of O ...
, 0.7% some other race, and 2.3% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino
''Hispanic'' and '' Latino'' are ethnonyms used to refer collectively to the inhabitants of the United States who are of Spanish or Latin American ancestry (). While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, for example, by the United States ...
of any race were 2.8% of the population.
There were 10,014 households, out of which 20.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 35.5% were headed by married couples living together, 8.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 52.7% were non-families. 39.2% of all households were made up of individuals, and 11.8% were someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.03, and the average family size was 2.75.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 16.6% under the age of 18, 7.7% from 18 to 24, 32.2% from 25 to 44, 27.6% from 45 to 64, and 15.9% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 40.3 years. For every 100 females, there were 94.2 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 92.6 males.
For the period 2010–2014, the city's estimated median annual household income was $67,679, and the median family income was $90,208. Male full-time workers had a median income of $58,441 versus $45,683 for females. The city's per capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
for the city was $42,724. About 4.0% of families and 7.6% of the population were below the poverty line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for t ...
, including 6.9% of those under age 18 and 7.1% of those age 65 or over.
Economy

Heinemann Heinemann may refer to:
* Heinemann (surname)
* Heinemann (publisher), a publishing company
* Heinemann Park, a.k.a. Pelican Stadium in New Orleans, Louisiana, United States
See also
* Heineman
* Jamie Hyneman
James Franklin Hyneman (born Se ...
USA is based in Portsmouth. Before its dissolution, Boston-Maine Airways
Boston-Maine Airways was an American airline headquartered in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, United States. It operated scheduled commuter services as well as Boeing 727 jet flights under the Pan Am Clipper Connection name. Its main base was Pease ...
(Pan Am Clipper Connection), a regional airline, was also headquartered in Portsmouth.
Companies with headquarters in Portsmouth include packaged software producer Bottomline Technologies and frozen yogurt maker Sweet Scoops.
Top employers
According to the city's 2020 Comprehensive Annual Financial Report, the top ten employers in the city are:Arts and culture
Sites of interest
Portsmouth Athenæum
The Portsmouth Athenæum is an independent membership library, gallery, and museum in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, United States. It preserves and provides access to an extensive collection of manuscripts, rare books, photographs, artworks and art ...
– a private membership library, museum and art gallery open to the public at certain times.
* Portsmouth Harbor Light
Portsmouth Harbor Lighthouse is a historic lighthouse located within Fort Constitution in New Castle, New Hampshire, United States.
History
The station was established in 1771 and was the 10th of 11 light stations established prior to the America ...
house – first established in 1771, the current structure was built in 1878 and is open for monthly tours from May through September.
* Prescott Park Arts Festival – summer entertainments in Portsmouth's waterfront park since 1974.
* Seacoast Repertory Theatre – founded in 1988, a professional theater troupe.
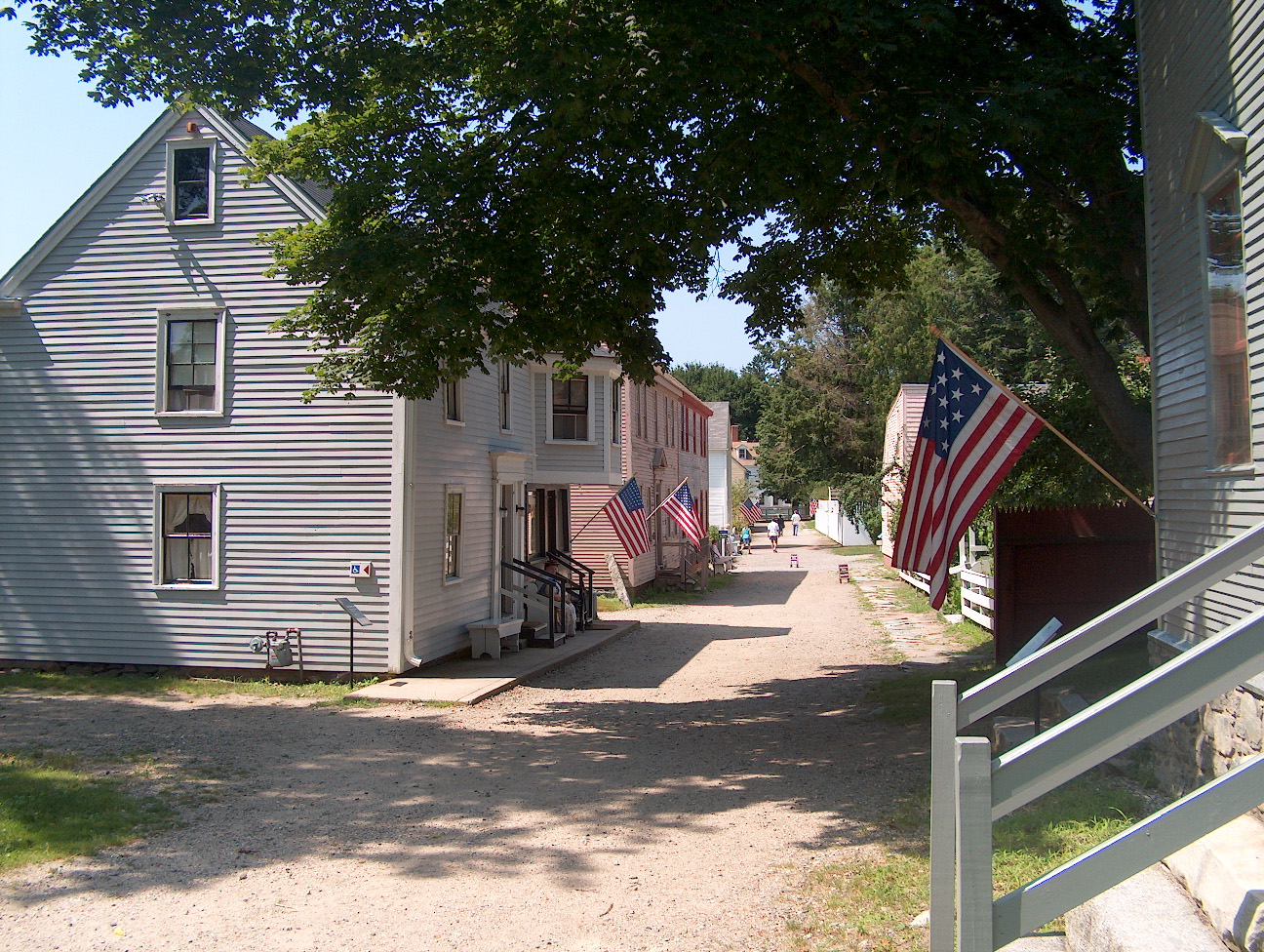
* Strawbery Banke Museum – a neighborhood featuring several dozen restored historic homes in Colonial, Georgian and Federal styles of architecture. The site of one of Portsmouth's earliest settlements.
* Whaling Wall – Painting of Isles of Shoals
The Isles of Shoals are a group of small islands and tidal ledges situated approximately off the east coast of the United States, straddling the border of the states of Maine and New Hampshire.
They have been occupied for more than 400 years, fi ...
Humpbacks created by Robert Wyland
Wyland (born July 9, 1956) is an American artist and conservationist best known for his more than 100 ''Whaling Walls'', large outdoor murals featuring images of life-size whales and other sea life to call attention to the plight of whales thro ...
, situated on the back of Cabot House Furniture. It is in disrepair, and restoration has not been allowed by the owners of Cabot Furniture.Choate, DavidWhaling Wall endangered
" September 14, 2010, Seacoast Online *Four public sculptures carved by Cabot Lyford stand in the city, including "The Whale" and "My Mother the Wind," a seven-ton blank granite statue which was installed on Portsmouth's waterfront in 1975. * Portsmouth African Burying Ground – a memorial park and the only archeologically verified 18th-century African burying ground in New England.
Historic house museums
John Paul Jones House
The John Paul Jones House is a historic house at 43 Middle Street in Portsmouth, New Hampshire. Now a historic house museum and a National Historic Landmark, it is where American Revolutionary War naval hero John Paul Jones, resided from 1781- ...
(1758)
* Governor John Langdon House
The Governor John Langdon House, also known as Governor John Langdon Mansion, is a historic mansion house at 143 Pleasant Street in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, United States. It was built in 1784 by Founding Father John Langdon (1741-1819), a me ...
(1784)
* Tobias Lear House (1740)
* Moffatt-Ladd House
The Moffatt-Ladd House, also known as the William Whipple House, is a historic house museum and National Historic Landmark in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, United States. The 1763 Georgian house was the home of William Whipple (1730–1785), a F ...
(also called William Whipple House) (1763)
* Rundlet-May House
The Rundlet-May House is a historic house museum at 364 Middle Street in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, Portsmouth, New Hampshire, United States. Built in 1807, it is a well-preserved example of a high-end Federal style mansion, built for a wealthy ...
(1807)
* MacPheadris-Warner House (1716)
* Wentworth-Coolidge Mansion (1750)
* Wentworth-Gardner House
The Wentworth-Gardner House is a historic mid- Georgian house, located at 50 Mechanic Street in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, United States. The house is operated as a museum by the Wentworth-Gardner Historic House Association. It is one of the fi ...
(also called Wentworth House) (1760)
* Henry Sherburne House
The Henry Sherburne House is a historic house at 62 Deer Street in Portsmouth, New Hampshire. Built about 1766, it is a well-preserved example of late Georgian architecture in the city, distinctive for its scrolled pediment entrance surrounded, t ...
(1766)
Sports
TheSeacoast United Phantoms
The Seacoast United Phantoms (formerly the New Hampshire Phantoms) are an American soccer team based in the coastal region of southeastern New Hampshire and northeastern Massachusetts. The team is based in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, where it p ...
are a soccer team based in Portsmouth. Founded in 1996, the team plays in the Northeast Division of USL League Two
USL League Two (USL2), formerly the Premier Development League (PDL), is a semi-professional developmental soccer league sponsored by United Soccer Leagues in the United States and Canada, forming part of the United States soccer league syst ...
(USL2), one of the unofficial fourth tier leagues of the American Soccer Pyramid.
Government
The city of Portsmouth operates under a council-manager system of government. Portsmouth elects a nine-member at-large City Council to serve as the city's primary legislative body. The candidate who receives the most votes is designated the Mayor (currently Deaglan McEachern), while the candidate receiving the second-highest vote total is designated the Assistant Mayor (currently Joanna Kelley). While the mayor and council convene to establish municipal policy, the City Manager (currently Karen Conard) oversees the city's day-to-day operations. Portsmouth is part ofNew Hampshire's 1st congressional district
New Hampshire's 1st congressional district covers parts of Southern New Hampshire and the eastern portion of the state. The district contains parts of Hillsborough, Rockingham, Merrimack, Grafton, and Belknap counties; and the entirety of ...
, currently represented by Democrat Chris Pappas. Portsmouth is part of the Executive Council's 3rd district, currently represented by Republican Janet Stevens
Janet may refer to:
Names
* Janet (given name)
* Janet (French singer) (1939–2011)
Surname
* Charles Janet (1849–1932), French engineer, inventor and biologist, known for the Left Step periodic table
* Jules Janet (1861–1945), French psych ...
. In the State Senate
A state legislature in the United States is the legislative body of any of the 50 U.S. states. The formal name varies from state to state. In 27 states, the legislature is simply called the ''Legislature'' or the ''State Legislature'', whil ...
, Portsmouth is represented by Democrat Rebecca Perkins Kwoka
Rebecca Perkins Kwoka (born September 1982) is an American politician who has served in the New Hampshire Senate from the 21st district since 2020. Her district encompasses Portsmouth, Durham, Newmarket, Lee, Newfields, Madbury, and Newingt ...
. In the State House of Representatives, Portsmouth is divided among the 25th through 31st Rockingham districts.
Politically, Portsmouth is a center of liberal politics and a stronghold for the Democratic Party. Ronald Reagan was the last Republican presidential nominee to carry the city in his 1984 landslide reelection. In 2016, Portsmouth voted 67.70% for Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
in the presidential election
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The pre ...
, 62.53% for Colin Van Ostern
Colin Van Ostern (born Kevin Colin O’Loughlin; February 14, 1979), is an American businessman and politician who served on the New Hampshire Executive Council from 2013 to 2017, where he represented the state's second district. He is a member o ...
in the gubernatorial election
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
, 64.48% for Maggie Hassan
Margaret Coldwell Hassan (; née Wood; born February 27, 1958) is an American politician and attorney serving as the junior United States senator from New Hampshire. A Democrat, Hassan was elected to the Senate in 2016 while serving as the 81st ...
in the senatorial election, and 62.16% for Carol Shea-Porter in the congressional election. In 2014, Portsmouth voted 70.05% for Maggie Hassan in the gubernatorial election
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
, 67.34% for Jeanne Shaheen
Cynthia Jeanne Shaheen ( ; née Bowers, born January 28, 1947) is an American retired educator and politician serving as the senior United States senator from New Hampshire since 2009. A member of the Democratic Party, Shaheen served as the 78 ...
in the senatorial election, and 68.34% for Carol Shea-Porter in the congressional election. In 2012, Portsmouth voted 67.56% for Barack Obama in the presidential election
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The pre ...
, 70.16% for Maggie Hassan in the gubernatorial election
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
, and 68.50% for Carol Shea-Porter in the congressional election.
In March 2014, Portsmouth became the first municipality in New Hampshire to implement protections for city employees from discrimination on the basis of gender identity, by a 9–0 vote of the city council.
Education
*Community College System of New Hampshire
The Community College System of New Hampshire (previously New Hampshire Community Technical Colleges (NHCTC) and prior to that New Hampshire Vocational Technical Colleges (NHVTC)) is an organization of seven public community colleges located thro ...
, Great Bay Community College
Great Bay Community College (GBCC) is a public community college in Portsmouth, New Hampshire. It is part of the Community College System of New Hampshire and is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education. The main campus is in ...
– Portsmouth campus
* Franklin Pierce University
Franklin Pierce University is a private university in Rindge, New Hampshire. It was founded as Franklin Pierce College in 1962, combining a liberal arts foundation with coursework for professional preparation.
The school gained university stat ...
– Portsmouth campus
* Granite State College – Portsmouth campus and on-site location at Great Bay Community College
Media
The Portsmouth Herald
''The Portsmouth Herald'' (and ''Seacoast Weekend'') is a six-day daily newspaper serving greater Portsmouth, New Hampshire. Its coverage area also includes the municipalities of Greenland, New Castle, Newington and Rye, New Hampshire; and Eli ...
''
Radio
* WSCA-LP Portsmouth Community Radio 106.1 FM *WHEB
WHEB (100.3 MHz) is a commercial FM radio station licensed to Portsmouth, New Hampshire, and serving the Seacoast Region of New Hampshire and Southern Maine. The station airs a mainstream rock radio format and is owned by iHeartMedia. WHEB b ...
100.3 FM rock formatted
Infrastructure
Transportation
The city is crossed by Interstate 95,U.S. Route 1
U.S. Route 1 or U.S. Highway 1 (US 1) is a major north–south United States Numbered Highway that serves the East Coast of the United States. It runs from Key West, Florida, north to Fort Kent, Maine, at the Canadian border, making ...
, U.S. Route 4
U.S. Route 4 (US 4) is a long United States highway that runs from East Greenbush, New York, in the west to Portsmouth, New Hampshire, in the east, traversing Vermont.
In New York, US 4 is signed North-South to reflect its alignment in the s ...
, New Hampshire Route 1A
New Hampshire Route 1A is an long state highway located in southeast New Hampshire. The route runs along the Atlantic coastline from the Massachusetts border north to Rye, then turns toward downtown Portsmouth. The southern terminus is at the Mas ...
, New Hampshire Route 16
New Hampshire Route 16 (NH 16) is a , north–south state highway in New Hampshire, United States, the main road connecting the Seacoast region to the Lakes Region and the White Mountains. Much of its length is close to the border with Maine. ...
, and New Hampshire Route 33
New Hampshire Route 33 is an east–west highway in the Seacoast Region of southeastern New Hampshire, connecting Stratham with Portsmouth. The western terminus is at New Hampshire Route 108 in Stratham. The eastern terminus is at U.S. Route 1 ( ...
. Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
is to the south, Portland, Maine
Portland is the largest city in the U.S. state of Maine and the seat of Cumberland County. Portland's population was 68,408 in April 2020. The Greater Portland metropolitan area is home to over half a million people, the 104th-largest metropo ...
, is to the northeast, and Dover, New Hampshire
Dover is a city in Strafford County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 32,741 at the 2020 census, making it the largest city in the New Hampshire Seacoast region and the fifth largest municipality in the state. It is the county se ...
, is to the northwest.
The Cooperative Alliance for Seacoast Transportation (COAST) operates a publicly funded bus network in the Seacoast region of New Hampshire and neighboring Maine including service in, to and from Portsmouth. C&J is a private intercity bus carrier connecting Portsmouth with coastal New Hampshire and Boston, as well as direct service to New York City. Wildcat Transit, operated by the University of New Hampshire
The University of New Hampshire (UNH) is a public land-grant research university with its main campus in Durham, New Hampshire. It was founded and incorporated in 1866 as a land grant college in Hanover in connection with Dartmouth College, m ...
, provides regular bus service to the UNH campus in Durham Durham most commonly refers to:
*Durham, England, a cathedral city and the county town of County Durham
*County Durham, an English county
* Durham County, North Carolina, a county in North Carolina, United States
*Durham, North Carolina, a city in N ...
and intermediate stops. The service is free for students, faculty and staff and $1.50 for the general public. Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous U.S. States and nine cities in Canada ...
's '' Downeaster'' train service, is available in Dover and Durham Durham most commonly refers to:
*Durham, England, a cathedral city and the county town of County Durham
*County Durham, an English county
* Durham County, North Carolina, a county in North Carolina, United States
*Durham, North Carolina, a city in N ...
, nearby to the northwest. Allegiant Air
Allegiant Air (usually shortened to Allegiant) is an ultra low-cost U.S. carrier that operates scheduled and charter flights. It is a major air carrier, the fourteenth-largest commercial airline in North America.
Allegiant was founded in 1 ...
offers scheduled airline service from Portsmouth International Airport at Pease
Portsmouth International Airport at Pease , formerly known as Pease International Airport, is a joint civil and military use airport located one nautical mile (2 km) west of the central business district of Portsmouth, a city in Rockingham ...
(PSM).
Sister cities
Portsmouth'ssister cities
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties.
While there are early examples of inter ...
are:
* Agadir
Agadir ( ar, أݣادير, ʾagādīr; shi, ⴰⴳⴰⴷⵉⵔ) is a major city in Morocco, on the shore of the Atlantic Ocean near the foot of the Atlas Mountains, just north of the point where the Souss River flows into the ocean, and south ...
, Morocco
* Carrickfergus
Carrickfergus ( , meaning " Fergus' rock") is a large town in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. It sits on the north shore of Belfast Lough, from Belfast. The town had a population of 27,998 at the 2011 Census. It is County Antrim's oldest ...
, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom
* Kitase, Ghana
* Nichinan, Japan
* Pärnu
Pärnu () is the fourth largest city in Estonia. Situated in southwest Estonia, Pärnu is located south of the Estonian capital, Tallinn, and west of Estonia's second largest city, Tartu. The city sits off the coast of Pärnu Bay, an inlet ...
, Estonia
* Severodvinsk
Severodvinsk ( rus, Северодвинск, p=sʲɪvʲɪrɐdˈvʲinsk) is a city in the north of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia, located in the delta of the Northern Dvina, west of Arkhangelsk, the administrative center of the oblast. As of the ...
, Russia
Portsmouth also has friendly relations with:
* Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
, England, United Kingdom
* Santarcangelo di Romagna
Santarcangelo di Romagna ( rgn, Santarcànzul) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Rimini, Emilia-Romagna, Italy, on the Via Emilia. As of 2009, it had a population of some 21,300. It is crossed by two rivers, the Uso and the Marecchia
...
, Italy
* Szolnok
Szolnok (; also known by other #Name and etymology, alternative names) is the county seat of Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county in central Hungary. A City with county rights, city with county rights, it is located on the banks of the Tisza river, i ...
, Hungary
Notable people
See also
* Portsmouth Public Library (New Hampshire) * 2006 Little League World Series, when a team from Portsmouth advanced to the quarter-finalsReferences
Further reading
* *External links
*Greater Portsmouth Chamber of Commerce
{{authority control Cities in New Hampshire Cities in Rockingham County, New Hampshire Former colonial and territorial capitals in the United States Populated places established in 1630 Populated coastal places in New Hampshire 1630 establishments in the Thirteen Colonies